Quality Attributes and Integral Quality of Transmitted Speech
 |
||
| Contents: | ||
The perceived overall quality of a speech communication system is one of the most important „Key Quality Indicators“ (KQI) for network providers. However, said indicator does not provide satisfactory information on the underlying cause for a quality degradation within the system. This project, consequently, focused on the diagnostic quality analysis of transmitted speech by breaking down the score for overall quality (“Mean Opinion Score”, MOS) into perceptual quality dimensions. Previous work by the collaborating institutions was able to show that speech quality can be modeled by the four following perceptual dimensions: “Noisiness”, “Coloration”, “Discontinuity”, and “Suboptimal Loudness”. All four dimensions are subjectively rated by test subjects during auditory listening experiments, but such ratings may also be estimated by applying instrumental models. Aim of this analytical approach is to directly trace back a degradation in speech quality to its corresponding technical cause within the network or the end-user device (root-cause analysis).
Dominating research questions of this project were the instrumental and robust estimation of the perceptive quality dimensions and underlying technical causes, and the identification of an interdependence between quality dimensions, technical causes, and overall quality. In this context, the following results are to be highlighted:
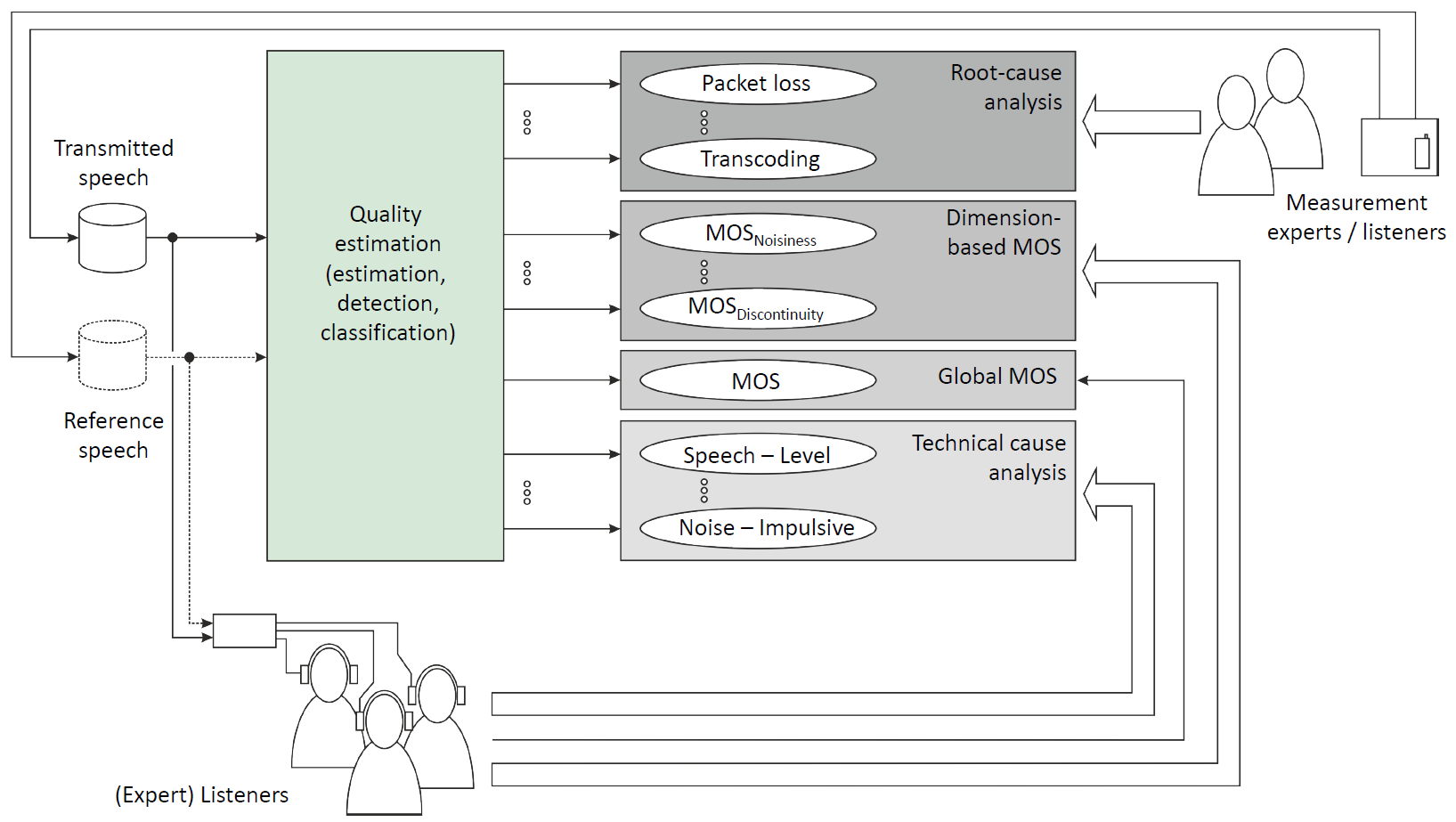 Within the scope of the reference-based estimation of the quality dimension, a novel and robust estimator for the dimension “Noisiness” was developed. By applying an algorithm which operates independently of the signal amplitude, the accuracy of the estimation is characterized by a maximum “epsilon-insensitive Root Mean Square Error” (RMSE*) of 0.22, a value that is well within the range required by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU-T). Additionally, there are promising results regarding the reference-free estimation of both the four quality dimensions and the overall quality. The current neural network approach already provides an accuracy within the range required by the ITU-T.
Within the scope of the reference-based estimation of the quality dimension, a novel and robust estimator for the dimension “Noisiness” was developed. By applying an algorithm which operates independently of the signal amplitude, the accuracy of the estimation is characterized by a maximum “epsilon-insensitive Root Mean Square Error” (RMSE*) of 0.22, a value that is well within the range required by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU-T). Additionally, there are promising results regarding the reference-free estimation of both the four quality dimensions and the overall quality. The current neural network approach already provides an accuracy within the range required by the ITU-T.
Technical causes considered in this project were mainly packet loss and speech coding effects, since these causes are most relevant for the industry partners (Deutsche Telekom AG, Rohde & Schwarz). Algorithms developed in the project are able to detect packet loss with an accuracy of 93 % and three bitrate classes of the AMR-WB codec with an accuracy of 95 %. Furthermore, a joint model was developed in order to robustly separate the two types of degradations. The model is able to quantitatively indicate the contribution of a technical cause to the observed overall quality degradation.
These and all other significant project results were published with international conferences conducting scientific quality control. If relevant, the results were both provided to industry partners and discussed at the ITU-T as contributions for the work items P.AMD and P.TCA. Moreover, some results are freely available online as executables.
Corresponding Publications
T. Hübschen, M. Gimm, G. Schmidt: A Background Noise and Impulse Response Corpus for Research in Automotive Speech and Audio Processing, Proc. DAGA, Germany, 2022
T. Hübschen, R. Al-Mafrachi, G. Schmidt: Impact of a Speaker Head Rotation on the Far-end Listening Situation, Proceedings of the 14th ITG Conference on Speech Communication, September 2021
S. Möller, T. Hübschen, T. Michael, G. Mittag, G. Schmidt: Non-intrusive Diagnostic Monitoring of Fullband Speech Quality, Proceedings of Interspeech 2020
T. Hübschen, B. Kaulen, M. Yurdakul, G. Schmidt: Sprachqualität in drahtlosen Ad-Hoc-Netzwerken, Proc. DAGA, Germany, 2019
G. Mittag, Louis Liedtke, Neslihan Iskender, Babak Naderi, T. Hübschen, G. Schmidt, S. Möller: Einfluss der Position und Stimmhaftigkeit von verdeckten Paketverlusten auf die Sprachqualität, Proc. DAGA, Germany, 2019
S. Möller, T. Hübschen, G. Mittag, G. Schmidt: Zusammenhang zwischen perzeptiven Dimensionen und Störungsursachen bei super-breitbandiger Sprachübertragung, Proc. DAGA, Germany, 2019
T. Hübschen, G. Mittag, S. Möller, G. Schmidt: Towards a Signal-based Root Cause Analysis Framework, Contribution 304, ITU-T SG12 Meeting, November 2018, Geneva
T. Hübschen, G. Mittag, S. Möller, G. Schmidt: Signal-based Root Cause Analysis of Quality Impairments in Speech Communication Networks, Proc. ITG, Oldenburg, Germany, 2018
S. Möller, T. Hübschen, G. Mittag, G. Schmidt: Diagnostic and Summative Approach for Predicting Speech Communication Quality in a Super-Wideband Context, Proc. ITG, Oldenburg, Germany, 2018
T. Hübschen, G. Schmidt: Bitrate and Tandem Detection for the AMR-WB Codec with Application to Network Testing, Proc. EUSIPCO 2018, Rome
T. Hübschen, M. Gimm, B. Kaulen, G. Mittag, S. Möller, G. Schmidt: Echtzeit-Rahmenwerk zur Unterstützung der Evaluierung von Sprachkommunikationssystemen, Proc. DAGA 2018 (online access)
